COLLISION RESOLUTION STRATEGIES
1.Open Addressing:
In an open addressing hashing system, if a collision occurs, alternative locations are tried until an empty location is found. Three techniques are commonly used for open addressing.
Features :
- All the identifiers are stored in the hash table itself
- Each slot contains an identifier or it is empty
- Requires a bigger table for open addressing
1. Linear Probing or Linear Open Addressing :
In this method, the hash address of identifier X is obtained. If the slot in its bucket is empty, the identifier is placed there. If an overflow occurs the identifier is placed in the next empty slot after its bucket.

Advantage
- It is a simple method of overflow handling.
- The method can be easily implemented using simple data structures like arrays.
Disadvantage
- An identifier whose bucket is full, will occupy the valid hash address of another identifier. Thus, one overflow will lead to many more.
- If an identifier is not found at its computed address, a series of comparisons will have to be made in order to retrieve it.
- If an identifier is not present in the bucket, the search will be terminated only the entire bucket is searched.
- It creates a cluster of identifiers i.e. identifiers are concentrated in some parts of the table.
- There is a possibility of the table becoming full.
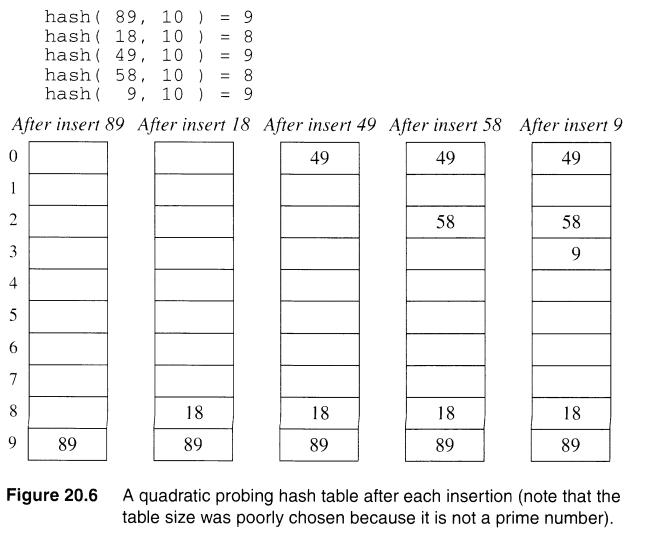
2.Quadratic Probing:
In Quadratic Probing a quadratic function of i is used as the increment. when the identifier is not found in its bucket , we search in successive buckets using an increment i.
The hash function is quadratic: this method checks the buckets number computed using a quadratic equation. This ensures that the identifiers are fairly spread out in the table.
Advantages :
- Avoids the clustering problem in linear probing to some extent
- Faster insertion and deletion
Disadvantages:
- There is no guarantee of finding an empty slot once the table becomes more than half full if the table size is not prime.
- Although this method eliminates primary clustering, it does not eliminate another phenomenon called “secondary clustering” in which different keys that hash to the same value follow the same rehash path.
3.Rehashing:
In this method, if an overflow occurs, a new address is computed by using another hash function.
A series of hash functions f1, f2, …..fn are used. To place an identifier X, f1(X) , f2(X) …..fm (X) are computed till an empty slot is found to place the identifier.
To search for identifier X, they are used in the same order to search the identifier. If all the hash functions have been used and the identifier is not found, it means that the identifier is not there in the table.

Advantages
- Does not lead to clustering
Disadvantages
- The process may loop forever. This may happen when some rehash function results in the same hash address for an identifier.
- It is difficult to find a series of hash functions yielding different addresses for the same identifier.
- Rehashing is costly as each rehash function takes a finite amount of time.
Heya just wanted to give you a quick heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different web browsers and both show the same results.
LikeLike