Introduction to JSX
You have never seen something like this before where HTML code gets engulfed inside my JavaScript code. And so, this is the special syntax that react to uses when it expresses the various react elements.
JSX is syntactic extensions to JavaScript which enables us to express react elements using it HTML like syntax. So, it is a shorthand notation from JavaScript functions that are called, which evaluate the JavaScript object. So, as we will see, the reason for approaching it this way as opposed to having the HTML separate from the JavaScrip code as done in other frameworks used to avoid the artificial separation of the rendering logic from the other UI logic. Very often, what is rendered in the screen is dependent upon the rest of the UI logic controlling the rendering on the screen.
So again, illustrating this with an example, you might see a react element being defined like this in the code. Now, then you’ll see this, you obviously notice immediately some HTML like syntax in the code, and some specification of attributes for the HTML like elements and so on. But in reality, this actually gets mapped in react into a corresponding JavaScript object here.

Configuring your React Application
Furthermore, the JavaScript part of Bootstrap cannot be directly used together with React. What Reactstrap supplies is Bootstrap components re-implement using React components. And so we can make use of them. Like for example, on the JavaScript-based components and Bootstrap have been re-implemented using React components in Reactstrap.
Configure your React Project to use Reactstrap
1.To configure your project to use reactstrap, type the following at the prompt to install reactstrap, and Bootstrap 4:
yarn add bootstrap
yarn add reactstrap
yarn add react-popper
You can also install the same using npm using the “npm install <package> –save” option if you are using npm instead of yarn.
2.Next, open index.js file in the src folder and add the following line into the imports:
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css';
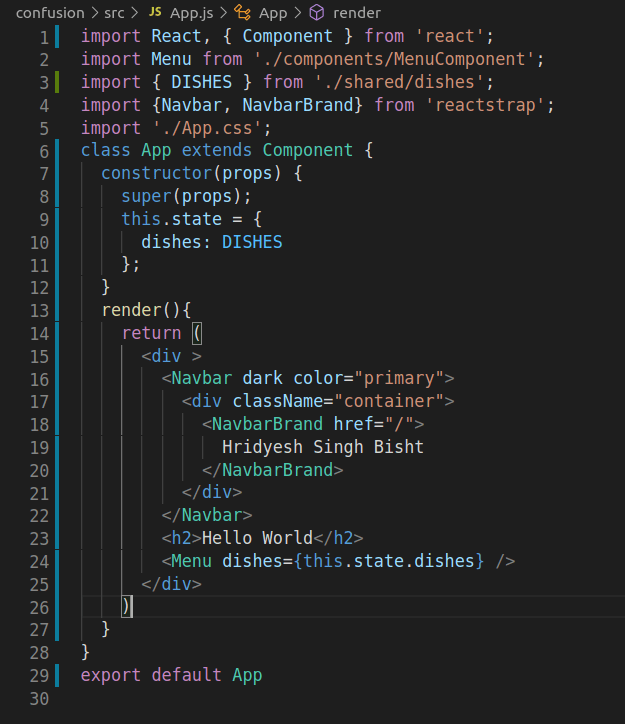
3.Open App.js in the src folder and update it as follows:
import React from 'react';
import {Navbar, NavbarBrand} from 'reactstrap';
import './App.css';
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<Navbar dark color="primary">
<div className="container">
<NavbarBrand href="/">
Hridyesh Singh Bisht
</NavbarBrand>
</div>
</Navbar>
<h2>Hello World</h2>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
For more Information,
- https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app
- https://reactstrap.github.io/
- https://reactjs.org/docs/introducing-jsx.html
React Components :
We can look at a component as a unit that returns a group of React elements that together render it part of the screen. So the components acts as a unit for gathering together a bunch of React elements with a common purpose.
Any component in React, a class component should implement this method called render() which will turn the corresponding view for this component. So, inside this render method, I need to return the view for this component. Also when you create the component, don’t forget to export that component from this file, because we would need to import this component wherever we want to make use of it within our application.
The app component that I’ve just created now becomes available within my app component. Now if I want to make use of the app component inside my component, all I need to do is go down and then simply state the exported variable with a self closing tack and that’s it.
When you declare the constructor, you would initialize a variable called this dot state which is a JavaScript object which contains all the state for this component. If you need to update the state of a component, you cannot directly go and update the state by changing the property values. Instead, any update to a state of the component has to be done through the use of that Sect State method.
FunctionName(parameter) {
this.setState({ variable: parameter});
}
Another way of passing information to a component is through Props. Each component can store its own local information in its state quote and quote. So this information is private and fully controlled within that component. Now is state within a component can easily be passed to its children through the use of props.
Now, the arrow function is used, if you want to pass some information or parameter back to the the event handler. If you don’t have any parameters or data to be passed back to the event handler, then you can simply say this. on. Some Function instead of defining it as the arrow function.
So for example, if several components have a shared state and any change to the state needs to be automatically seen by all these components, then it is better to move the state to one of the ancestors, common ancestor of all these components, and ensure that any state changes will be sent back up to that common ancestor. Any changes to data in one component may need to be reflected to another component, and this is where by lifting the state up it makes it more convenient for you to handle this. When you have an array of items, you could easily lay them out as list in your react components. Lists and the way you handle them is very similar to JavaScript.
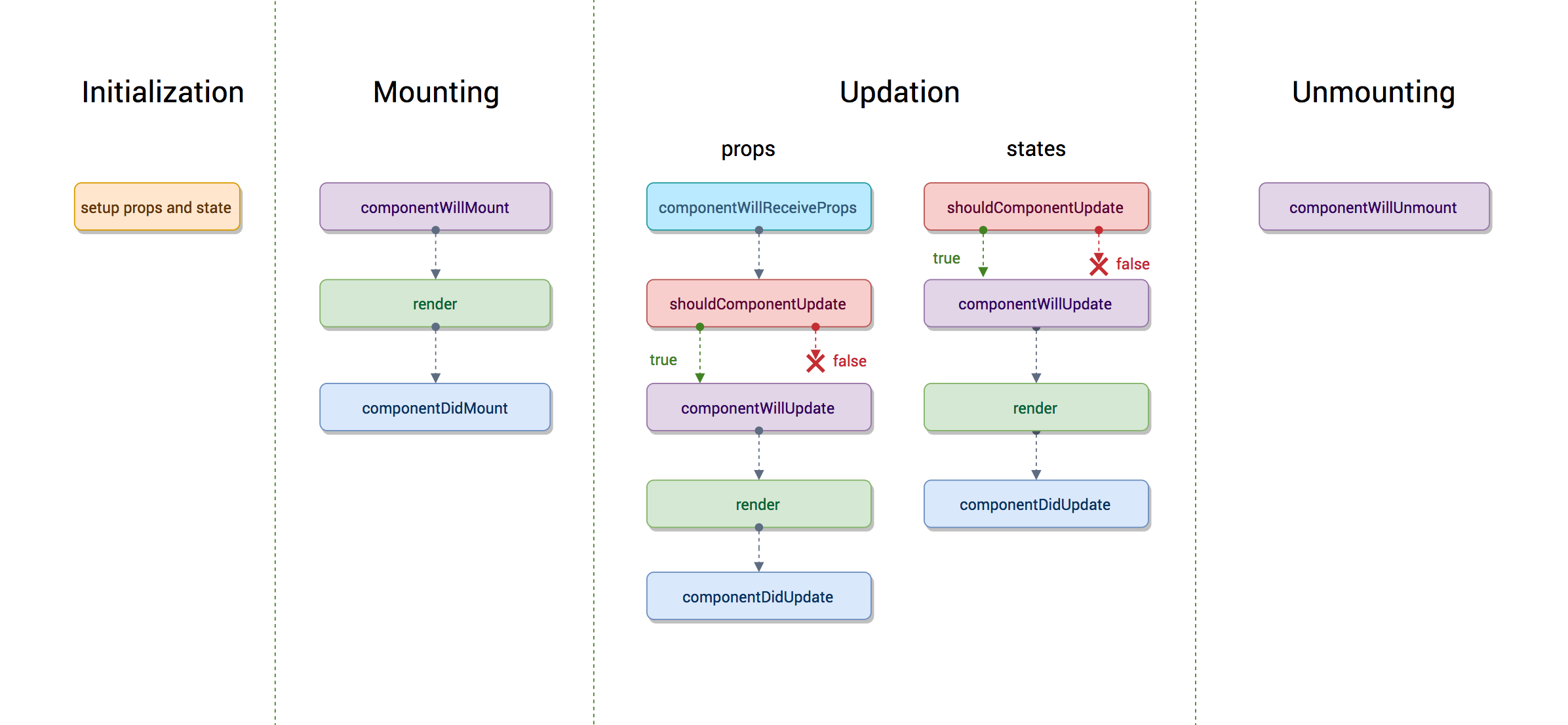
Life cycle of the component:
Each React component as in when it is required will be created by React and then added into the DOM of your entire application. So, every time a React component needs to be included into your applications view, then the component that hosts the specific part of the view will be created and added into the overall React component hierarchy.
The life cycle for the component,
- Initially, the component doesn’t exist,
- then the component gets created and then once it is created,
- then it can be mounted into your React application at an appropriate point in the hierarchy of components,
- then it will exist at that point for a period of time and
- then subsequently, maybe you no longer require that view, and so at the point, the component can be removed from this hierarchy.
When a component is being updated, there are several lifecycle methods associated with this process. So these lifecycle methods are called when a component is being re-rendered or being updated. Now, this could be caused either because the props that are supplied to the component changed, or the internal state of the component changed.
So, as you realize, a component passes through a life cycle of creation, mounting, and then existing in the hierarchy, then unmounting, and then disappearing at the point.
Thanks for this article, it is totally useful and super informative!
To be honest, normally I choose React Native, it is something quite similar, but there are some important differences between these two languages. It is not only clear and easy to learn but functional as hell! If you want, you can read more about this language here: https://www.miquido.com/blog/is-react-native-the-right-choice-for-your-business/
LikeLike