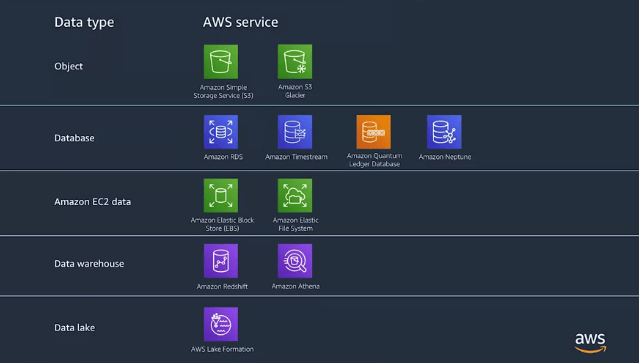
Data Storage :
We got a lot of data that an EC2 is processing, and we need somewhere to store it. We could just archive it, but that’s only if data is not needed immediately.
Q. Does data need to be accessed quickly? Or less? Does it need to be stored for days, months or years? Even what type of data you’re storing? Are you storing objects, rose, time-series data or any of the other types?
1.Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) :
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Amazon S3 provides easy-to-use management features so you can organize your data and configure finely-tuned access controls to meet your specific business, organizational, and compliance requirements. More information on Amazon S3 is available at: https://aws.amazon.com/s3/
2.Amazon S3 Glacier :
Amazon S3 Glacier is a secure, durable, and extremely low-cost cloud storage service for data archiving and long-term backup. It is designed to deliver 99.999999999% durability, and provides comprehensive security and compliance capabilities that can help meet even the most stringent regulatory requirements. More information on Amazon S3 Glacier can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/glacier/
3.Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) :
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud. It provides cost-efficient and resizable capacity while automating time-consuming administration tasks such as hardware provisioning, database setup, patching and backups.
Amazon RDS is available on several database instance types – optimized for memory, performance or I/O – and provides you with six familiar database engines to choose from, including Amazon Aurora, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle Database, and SQL Server. You can use the AWS Database Migration Service to easily migrate or replicate your existing databases to Amazon RDS. More information on Amazon RDS can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/rds/
4.Amazon DynamoDB :
Amazon DynamoDB is a key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. It’s a fully managed, multi region, multi master database with built-in security, backup and restore, and in-memory caching for internet-scale applications. DynamoDB can handle more than 10 trillion requests per day and can support peaks of more than 20 million requests per second. More information on Amazon DynamoDB can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/
5.Amazon Time-stream :
Amazon Time-stream is a fast, scalable, fully managed time series database service for IOT and operational applications that makes it easy to store and analyze trillions of events per day at 1/10th the cost of relational databases. Details on Amazon Time-stream can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/timestream/
6.Amazon Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB) :
Amazon QLDB is a fully managed ledger database that provides a transparent, immutable, and cryptographic verifiable transaction log owned by a central trusted authority. Amazon QLDB tracks each and every application data change and maintains a complete and verifiable history of changes over time.
Amazon QLDB is a new class of database that eliminates the need to engage in the complex development effort of building your own ledger-like applications. With QLDB, your data’s change history is immutable – it cannot be altered or deleted – and using cryptography, you can easily verify that there have been no unintended modifications to your application’s data. Details about Amazon QLDB can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/qldb/
7.Amazon Elastic Block Store :
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is an easy to use, high performance block storage service designed for use with Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for both throughput and transaction intensive workloads at any scale. A broad range of workloads, such as relational and non-relational databases, enterprise applications, containerized applications, big data analytics engines, file systems, and media workflows are widely deployed on Amazon EBS. More information on Amazon EBS is available at: https://aws.amazon.com/ebs/
8.Amazon Elastic File System
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) provides a simple, scalable, elastic file system for Linux-based workloads for use with AWS Cloud services and on-premises resources. Amazon EFS is well suited to support a broad spectrum of use cases from highly parallelized, scale-out workloads that require the highest possible throughput to single-threaded, latency-sensitive workloads. Use cases such as lift-and-shift enterprise applications, big data analytics, web serving and content management, application development and testing, media and entertainment workflows, database backups, and container storage. More information about Amazon EFS can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/efs/
9.Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift extends data warehouse queries to your data lake, with no loading required. You can run analytic queries against petabytes of data stored locally in Redshift, and directly against exabytes of data stored in Amazon S3. It is simple to set up, automates most of your administrative tasks, and delivers fast performance at any scale. Information about Amazon Redshift is available at: https://aws.amazon.com/redshift/
10.Amazon Athena
Amazon Athena is an interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL. Athena is serverless, so there is no infrastructure to manage, and you pay only for the queries that you run.
Athena is easy to use. Simply point to your data in Amazon S3, define the schema, and start querying using standard SQL. Most results are delivered within seconds.Details about Amazon Athena can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/athena/
Data Transfer :
1.AWS Snowball :
Snowball is a petabyte-scale data transport solution that uses devices designed to be secure to transfer large amounts of data into and out of the AWS Cloud. Snowball devices use tamper-resistant enclosures, 256-bit encryption, and an industry-standard Trusted Platform Module (TPM) designed to ensure both security and full chain-of-custody for your data. More information about AWS Snowball can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/snowball/
2.AWS Snowmobile :
AWS Snowmobile is an Exabyte-scale data transfer service used to move extremely large amounts of data to AWS. You can transfer up to 100PB per Snowmobile, a 45-foot long ruggedized shipping container, pulled by a semi-trailer truck. Snowmobile makes it easy to move massive volumes of data to the cloud, including video libraries, image repositories, or even a complete data center migration. Transferring data with Snowmobile is more secure, fast and cost effective. Information about how to get started with AWS Snowmobile can be found at: https://aws.amazon.com/snowmobile/
Encryption and Security :
1.Encryption in Transit :
Handling customer data without thinking ahead on how to secure it can impact credibility of your organization and your company
- Define requirements for data protection in transit. Based on legal and compliant requirements, you classify data into multiple categories which is dependent on sensitivity level of the data.
- Then you apply encryption standards to the right category. For example, historical weather data is consider public data. So you don’t have to require encryption in transit when working with this data. However, customer credit card information is highly confidential data, thus you want to make sure is encrypted in transit.
- You also need to authenticate network communications. So that includes verifying the identity of communications by using protocol such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) or using IPSec.
- IPSec can be implemented when you set up virtual private network or VP N to create a secure connection between your VPC and on-premises Network.
- Transport Layer Security or TLS is a set of industry standard cryptographic protocols used for encrypting information at the transport layer which is layer four of the OSI model.
- Both SSL and TLS negotiate a symmetric key between the client and a server that are used to encrypt data flowing between two entities.
- You should use HTTPS instead of HTTP for data transmission. HTTPs use SSL, TLS protocol to prevent eavesdropping, unauthorized alterations, and unauthorized copying of your data.
Internet Protocol Security or IPSec is a protocol for intrinsic data protection between host. It is a protocol to protect communication at the network layer which is layer three of the OS I model.
All AWS services provide API endpoints that allow you to establish secure HTTPS communication sessions. For your web application, you can choose to terminate the encryption at the application layer or at the load balancer layer. You want to make sure you store X.509 certificates securely and rotate them with strict access control. Amazon Certificate Manager (ACM) handles the complexity of creating and managing public SSL and TSL certificate for your website and applications. You can use public certificates provided by ACM called ACM certificates or certificate that you import into ACM.
2.Encryption at Rest :
There are two services we’re going to touch on here. Think about your key? Do you want to manage it, or do you want to AWS to manage it? Do you want it to also be created by AWS, so that you can let us do the heavy lifting of generating new keys on a fixed schedule?
These kinds of questions lead us to Amazon key management service or KMS, which will allow you to easily manage the encryption keys used to encrypt your data. The primary resource here is called a customer master key and you use that to encrypt and decrypt up to four kilobytes of data.
- These CMKs can be managed by you, which will give you full control of them. You manage everything from rotation to deletion, IAM policies, and so forth.
- AWS managed and these are created, managed, and used on your behalf by an AWS service that integrates with KMS
- Both of these types live in your AWS account, whereas the third type called AWS owned lives outside your AWS account. Think of them as part of a collection of CMKs that AWS owns and manages for use in multiple AWS accounts.
Q. What if your company wants you to manage these keys using dedicated hardware?
AWS CloudHSM is a cloud-based hardware security module (HSM) that enables you to easily generate and use your own encryption keys on the AWS Cloud. With CloudHSM, you can manage your own encryption keys using FIPS 140-2 Level 3 validated HSMs. CloudHSM offers you the flexibility to integrate with your applications using industry-standard APIs, such as PKCS#11, Java Cryptography Extensions (JCE), and Microsoft CryptoNG (CNG) libraries.

3.Database encryption :
You can use SSL from your application to encrypt a connection to an RDS DB Instance running Amazon Aurora, MySQL, MariaDB, SQL Server, Oracle or Postgres. Each DB engine has it own process of implementing SSL.
In case you are wondering, Amazon Aurora is a relational database service which features are distributed fault tolerant, self-healing storage system that can auto scale up to 64 terabytes per database instance. The best part is, it is compatible with MySQL and Postgres database engines. You can encrypt your Amazon RDS, DB Instance and snapshot addressed by enabling the encryption option when you create Amazon RDS DB Instance. RDS encrypted DB Instance use the industry standards AES-256 encryption algorithm to encrypt your data on the server that hosts your DB Instance.
Amazon DynamoDB encrypts all user data, store in DynamoDB table by default. Server side encryption at rest is enabled for all DynamoDB table data and can not be disabled. When a table is encrypted, all the data includes as primary key, index, stream, Global table, backups will be encrypted.
Encryption at rest integrate with AWS KMS for managing the encryption key that is used to encrypt your tables and you can switch between keys.
1.S3 :
Recommendations for S3 Storage Bucket .
- only allowing bucket access to authorized parties.
- if you don’t need public access, make sure it’s disabled for a bucket.
- maybe you want to add encryption to the equation.
A bucket policy is a resource-based AWS Identity and Access Management policy, which means that you designate access permissions for the bucket and the objects in it. It is recommend to enable default encryption on the bucket itself. This means that all objects in that bucket will be encrypted, and that encryption can be centrally managed at the bucket level. Objects will be encrypted using server-side encryption with either Amazon S3 managed keys, that’s SSE-S3, or AWS KMS, or Key Management Service managed keys, SSE-KMS.
When you use server-side encryption, Amazon S3 encrypts an object before saving it to disk in its data centers and decrypts it when you download the objects. More details on using Encryption with Amazon S3 can be found at: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/bucket-encryption.html
4.Amazon Macie :
That means Amazon Macie will automatically recognize your sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information, or PII, even intellectual property, your IP, You’ll then be provided with alerts on areas of interest, along with a dashboard giving you insights into how your data is being accessed, moved, and modified.
Some of the things that Macie checks for are
- inadvertent exposure of data, insider threats, and targeted attacks.
- You can then alert on suspicious activity, such as compromised user accounts and downloading of large amounts of sensitive content from unusual IP addresses,
- maybe the download of a large quantity of source code by a user account that typically does not access this type of sensitive content.
The fully managed service continuously monitors data access activity for anomalies, and generates detailed alerts when it detects risk of unauthorized access or inadvertent data leaks. Currently, Amazon Macie is available to protect data stored in Amazon S3. More information about Amazon Macie is available at: https://aws.amazon.com/macie/
5.EBS Encryption :
EBS provides persistent block storage volume for use with Amazon EC2 instance in the AWS cloud. When you need to encrypt data in an EBS volume, the solution is straight forward. You can configure your AWS account to enforce the encryption of new EBS volume and snapshots. That means, new EBS volume will be automatically encrypted when you create them. EBS provides our features to backup data in EBS volume to ash tree by taking point-in-time snapshots.
When you create encryption by default, these snapshots will be encrypted as well. EBS volume encryption doesn’t require you to build, maintain, and secure your old key management infrastructure. Instead, they AWS key management service or KMS when creating encrypted volumes as snapshot.
For assisting UN-encrypted EBS volume, you can create snapshots for the volumes, and create new encrypted EBS volume from this snapshot using “Create Volume” or “Copy Snapshot” API action. When you create an encrypted EBS volume and attach it to a supported instant type, the following type data are encrypted.
- course data address inside the volume.
- all data are moving between the volume and the instant will be encrypted.
- all the snapshot created from the volume will be encrypted as well.
- all the volume created from those snapshot also encrypted.
Encryption operation occur on the servers that host EC2 instance, ensuring the security of both data address and data in transit between an instant and it’s attach EBS storage. Amazon EBS encryption is available only on certain instant types. You can attach both encrypted and unencrypted volumes to a supported instance type.

One thought on “AWS Fundamentals: Addressing Security Risk”