Low-code development simplifies creating apps by reducing manual coding through prebuilt components and visual workflows. Unlike no-code platforms, low-code platforms offer more customization and control, making them suitable for both developers and business users.
Key benefits:
- Speed: Faster development cycles.
- Collaboration: Easier participation for business users.
- Adaptability: Quick response to changing requirements.
- Scalability: Built-in tools for scaling apps effectively.
This blog explores when to choose OutSystems over high-code, compares OutSystems with high-code. It focuses on how both approaches can be combined for flexible, scalable app development.
How to use Outsystems
OutSystems is a leading low-code platform that simplifies web and mobile app development. It provides tools for rapid app creation, making it easier for developers to build and deploy applications efficiently.
Key features:
- External Integrations: Seamlessly connect to third-party services, data, and APIs.
- Built-in Management and Analytics: Monitor and optimize app performance.
OutSystems offers two platforms:
- OutSystems 11: Designed for enterprise-grade web and mobile apps with on-premises and cloud deployment options.
- OutSystems Developer Cloud (ODC): A modern cloud-native platform focused on serverless architecture, enhanced collaboration, and faster development cycles.
Choosing Between OutSystems 11 and OutSystems Developer Cloud:
| Feature | OutSystems 11 (O11) | OutSystems Developer Cloud (ODC) |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment Model | On-premises and cloud | Cloud-native, serverless |
| Security and Scalability | Enterprise security tools | Built-in security, disaster recovery |
| Development Environment | Service Studio | ODC Portal |
| Dependency Management | Module-based, strong dependencies | Simplified dependencies, no modules |
| App Management | LifeTime, Service Center | ODC Portal |
Since O11 offers a free tier for exploration, this blog focuses on it. Similar to a web app, lets break down building web apps into 3 sections:
- Building UI
- Managing data
- Implementing logic
Building UI
The OutSystems Service Studio provides a visual development environment for creating UIs. Key UI-building components include:
- Screen Templates: Pre-built templates combining UI and logic.
- UI Patterns: Reusable design components ensuring consistency.
- Widgets: Drag-and-drop elements like buttons and input fields.
- Forge Components: Community-contributed extensions for enhanced functionality.
Advantages over High-Code:
- Drag-and-drop components instead of coding from scratch.
- Reusable patterns ensure design consistency.
- Built-in cross-browser compatibility testing.
- Custom CSS and JavaScript support for advanced styling.
Managing data
OutSystems provides tools for efficient data management:
- Entities: Persistent storage for structured data.
- Structures: Handle complex or temporary data types (similar to enums).
- Aggregates: Visual tools for querying and filtering data(similar to SQL but UI driven).
- SQL: Use SQL queries for custom data access.

Advantages over High-Code:
- Simplify complex schema design using the entity diagram tool.
- Integrate external data sources without manual type conversions.
- Validate data with built-in functions.
Implementing logic
OutSystems 11 offers visual tools for application logic:
- Server and Client Actions: Event-driven logic handling.
- Data Refresh Mechanisms: Real-time data synchronization.
- Conditions and Loops: Support for conditional execution and iteration.

Advantages over High-Code:
- Define workflows visually without manual scripting.
- Built-in scalability tools reduce architectural planning.
- Easier debugging with visual representations of logic.
Publishing app
To publish your app in O11, follow these steps:
- Select the 1-Click Publish button.
- The app uploads to the server.
- The server generates, compiles, and deploys the code to the application server.
- The server updates the database to synchronize the logic and data model, if needed.
High-Code publishing process:
- Manually compile code using external build tools.
- Manage dependencies separately.
- Configure deployment pipelines manually.
- Update databases with custom scripts.
Simplified OutSystems publishing process:
- Automatic Database Synchronization: Updates schema and data models automatically.
- Automated Build and Deployment: Handles compiling, building, and deploying automatically.
- Built-in Dependency Management: Manages module dependencies internally.
- Integrated CI/CD: Offers version control, CI/CD, and environment promotion tools.
OutSystems vs. traditional high-code approaches:
There are not a lot of differences, when it comes to builiding a web app. Just a difference of terminologies:
| Component | OutSystems 11/ODC | High-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Front-End | Visual UI Editor | HTML, CSS, JS |
| Back-End Logic | Visual Logic Editor | Python, JavaScript |
| IDE | Service Studio | VS Code, IntelliJ |
| Automation Tools | Built-in Workflows | Airflow, Custom Code |
| Libraries/Extensions | Forge Marketplace | Pip, npm |
Integrating low and high code
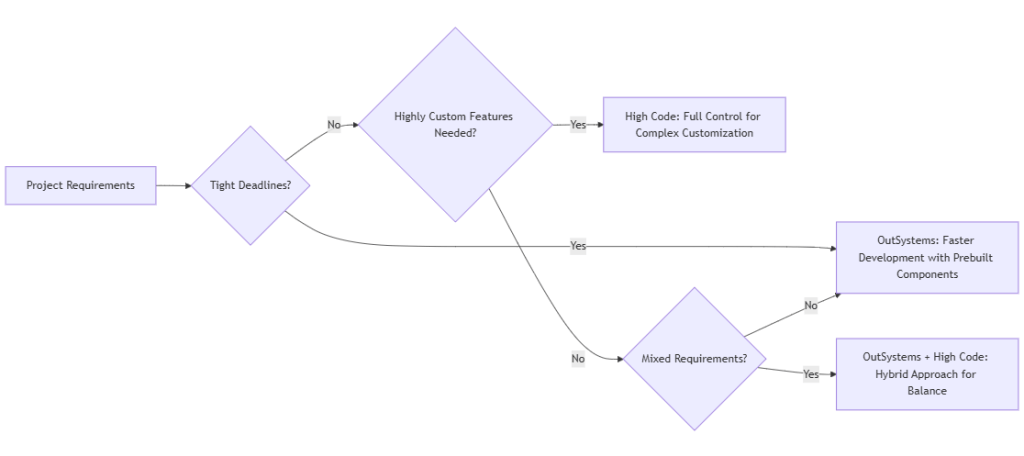
Low-code platforms enable fast development with minimal coding, making them ideal for non-developers or projects with tight timelines. High code requires more technical expertise, offering greater customization and control over complex features.
Combining low-code and high-code provides flexibility and speed. However, successful integration requires a clear strategy.
For example:
- Integrate an external API using ODC Integration Builder for standard use cases.
- Use custom JavaScript actions for advanced data processing.
For more information, refer to Integrating Low-Code & High-Code Solutions Effectively.