1.Circular List
A Circular list , has the next of last node pointing towards the first node of the list , so in algo terms :
rear->next =front;
This forms a circle of nodes as now last node and first node is connected , just like a circle :
Now why Circular Link list , as you might have noticed when you pop a value the memory of the element goes waste , until an unless you free the memory location , So to counter this we use circular List .
Class’s look like ,
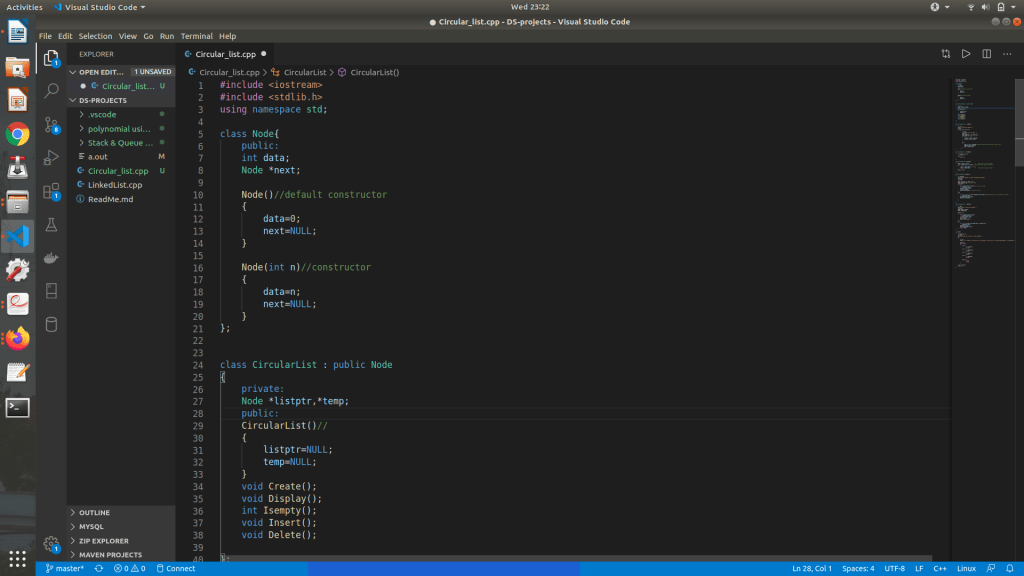
Code is going to be similar to linked list , except the condition to iterate through the list, we can’t use NULL as there will not be a NULL Value , so we use last ptr or listptr , it point as the last node .
void CircularList :: Create()//Same as Linked list
{
int i, n;
cout<<"\n How many nodes :";
cin>>n;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
int num;
cout<<"\n Enter the data :";
cin>>num;
Node *newnode = new Node(num);
if(listptr == NULL)
{
listptr = temp = newnode;
newnode->next=listptr;//for last node to point to first node
}
else
{
temp -> next = newnode;//temp currently points towards current block
newnode->next=listptr;//for last node to point to first node
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
void CircularList:: Display()
{
Node * temp = listptr ; /* temp points to first node*/
while (temp->next != listptr) //iterate till it reaches last block
{
cout << temp->data << "--->";
temp = temp->next; /* move temp to the next node */
}
cout<< "END";
}
void CircularList::Insert()
{
int num,pos;
cout<<"Enter number to input followed by position";
cin>>num;
cin>>pos;
Node *newnode= new Node (num);
Node *temp=listptr;//value of head
if(pos==1)//first node
{
while (temp->next!=listptr)//to reach last node
temp=temp->next;
newnode->next=listptr;
listptr=newnode;
temp->next=newnode; //link last to first
}
else
{
for (int i = 1; i < pos-1 &&temp->next!=listptr; i++)//reaching till the location to insert ,
temp=temp->next;
newnode->next=temp->next;
temp->next=newnode;
}
}
void CircularList :: Delete()
{
int pos;
cout<<"Enter position to delete" ;
cin>>pos;
Node *temp= listptr;
Node *temp1=temp;
if(pos == 1)
{
while (temp1->next!=listptr)
temp1=temp1->next;
listptr=listptr->next;
delete temp;
temp->next=listptr;
}
else
{
for (int i=1;i<pos-1 && temp->next !=listptr;i++)
temp=temp->next;
temp1=temp->next;
temp->next=temp1->next;
delete temp1;
}
}
2.Doubly Linked list :
A Doubly Linked list , is a simple linked list which also contains address of it’s previous node , So we can iterate to both side while iterating ,
When we reverse a Link list it takes a lot of computational power , just to reduce it we take prev as well as next address values , for easy iteration .
Now class’s are going to be similar , but will contain an extra variable in class Node , Node *prev,
A.Here you can Insert a node in three Scenarios ,
1.At beginning
int ele;
cout<<"\n Enter an element ";
cin>>ele;
Node *newnode = new Node(ele);
newnode->next=lp;
lp->prev=newnode;
lp=newnode;
return lp;2.At Middle
Node *current_node=lp;
int count=1;
while (current_node->next!=NULL)
{
if(count==pos)
{
int ele;
cout<<"\n Enter an element ";
cin>>ele;
Node *newnode = new Node(ele);
newnode->next=current_node->next;
current_node->next->prev=newnode;
current_node->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=current_node;
break;
}
else
count+=1;
current_node=current_node->next;
}3.Insert at END
Node *current_node=lp;
while (current_node->next!=NULL)
current_node=current_node->next;
int ele;
cout<<"\n Enter an element ";
cin>>ele;
Node *newnode = new Node(ele);
newnode->next=NULL;
current_node->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=current_node;B.You can delete node in three scenarios ,
1.Deleting first node
if(lp==NULL)
cout<<"\n List is Empty";
else
{
Node *tempo=lp;
lp=lp->next;
free(tempo);
return lp;
}2.Deleting Middle node
if(lp==NULL)
cout<<"\n List is Empty";
else
{
Node *current_node=lp;
int count=1;
while (current_node->next!=NULL)
{
if(count==pos)
{
Node *tempo;
tempo->prev->next=tempo->next;
tempo->next->prev=tempo->prev;
free(tempo);
break;
}
else
count+=1;
current_node=current_node->next;
}
}3. At the last node
if(lp==NULL)
cout<<"\n List is Empty";
else
{
Node *current_node=lp;
while ((current_node->next)->next!=NULL)
current_node=current_node->next;
Node *tempo=current_node->next;
current_node->next=NULL;
free(tempo);
}
}GitHub code :https://github.com/kakabisht/Data-structures
One thought on “Types of Lists :”